Updated on September 8, 2025
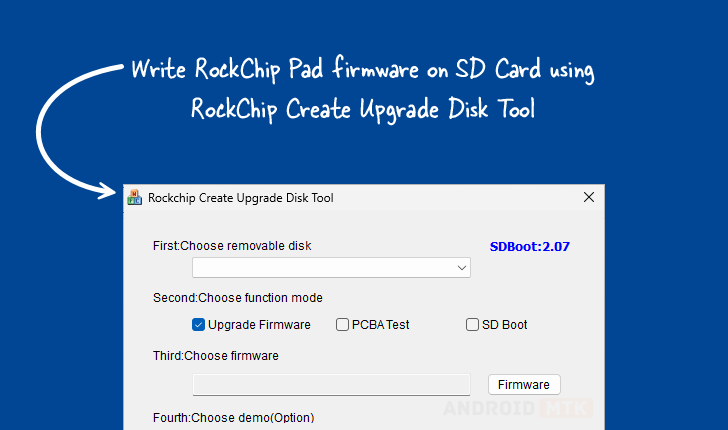
The Rockchip Create Upgrade Disk Tool represents a pivotal utility for developers, technicians, and advanced users operating within the Rockchip ecosystem, providing granular control over the crucial initial stages of device operation. This specialized Windows application is engineered primarily to facilitate the secure and precise writing of Rockchip boot firmware directly onto external storage media, most commonly SD cards. Its significance lies in its robust capabilities that extend beyond simple file transfer, enabling comprehensive management of the storage structure necessary for initializing Rockchip-powered single-board computers (SBCs), development kits, and various embedded systems. By mastering this tool, users gain the capacity to establish bootable media capable of system recovery, initial operating system deployment, or sophisticated hardware testing protocols.
The core functionality revolves around transforming a standard SD card into a precisely configured boot medium. This process necessitates a deep understanding of low-level storage architecture, which the tool abstracts through a user-friendly interface, yet preserves access to underlying controls. The ability to manage both physical and logical partitions is central to its utility, offering developers the flexibility to delineate distinct areas on the storage device for specific functions—such as maintaining a read-only bootloader partition alongside a larger, writable data or system image partition. This level of partitioning control is vital for ensuring boot integrity and facilitating iterative development cycles without corrupting essential boot records.
The underlying architecture of many embedded systems relies heavily on the precise configuration of the bootloader stored on removable media before the main internal storage is initialized or accessed. Rockchip processors, prevalent in tablets, media players, and IoT devices, require specific firmware images to transition from a powered-off state to executing the primary operating system kernel. The Create Upgrade Disk Tool serves as the bridge, ensuring that the necessary boot sectors and initial system components are written flawlessly, mitigating the risks associated with less specialized flashing utilities.
In-Depth Examination of Core Features
The Rockchip Create Upgrade Disk Tool is equipped with a suite of features, each meticulously designed to address specific requirements in the firmware deployment and testing lifecycle for Rockchip hardware. These features collectively transform a basic flashing utility into a comprehensive device preparation suite.
Precision Firmware Writing
At its heart, the tool excels at the direct inscription of Rockchip boot firmware. This is not merely copying files; it involves sector-by-sector writing of binary images that contain the crucial bootloader code. The utility demonstrates broad compatibility, accepting various firmware formats common within the Rockchip development community. This feature ensures that the necessary low-level instructions—which tell the processor how to initialize critical hardware components like RAM, clock systems, and peripheral controllers—are installed correctly. Successful bootloader installation is the prerequisite for any subsequent OS loading or advanced diagnostics. Errors at this stage render the target device inoperable, highlighting the necessity of a reliable writing mechanism like this dedicated tool.
Advanced Partition Scheme Management
The capability to manipulate both physical and logical partitions is a hallmark of professional-grade flashing utilities. Physical partitioning refers to defining the hard boundaries on the storage device, dictating the total available space allocated to different structures recognized by the system’s firmware. Logical partitioning, on the other hand, often relates to defining how the operating system or bootloader perceives and accesses these segments. For instance, a developer might use this feature to create a small, immutable FAT32 partition for the bootloader and a larger, perhaps ext4 or user-specific, partition for the main system image. This precise organization maximizes storage efficiency and enhances system robustness by isolating critical boot components from potentially volatile user data areas.

Multi-Mode Operational Flexibility
The tool’s versatility is significantly enhanced by its support for multiple operational modes, catering to distinct phases of the device lifecycle.
- Firmware Upgrade Mode: This is the standard procedure for flashing a new or updated operating system environment onto the SD card, intended for immediate use in a target device.
- PCBA Testing Mode: This specialized mode is invaluable during the manufacturing or quality assurance phases. It allows engineers to flash diagnostic firmware directly onto the SD card, enabling testing of the Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) itself—verifying hardware functionality independent of the final OS configuration. This is crucial for early fault detection.
- SD Boot Option: This mode focuses specifically on configuring the storage medium to be recognized by the Rockchip boot ROM as the primary source for initial system execution. This bypasses internal eMMC or NAND storage, making the SD card the temporary, active system drive.
This adaptability ensures that the tool remains relevant whether the user is deploying a final product image or conducting deep hardware diagnostics.
Selective Data Inscription Control
Beyond writing monolithic image files, the Create Upgrade Disk Tool grants users the power of selective data writing. This feature allows for targeted injection of specific files, configuration blobs, or even partial images into pre-defined partitions or sector ranges on the SD card. This level of control is essential when only a small component—such as a configuration file, a custom kernel module, or a security certificate—needs updating without requiring a full re-flash of the entire system image. Precision in data placement minimizes the risk of unnecessary data overwrites and significantly accelerates iterative testing loops.
Real-Time Process Visualization
To maintain user confidence during potentially lengthy write operations that directly affect core device functionality, the tool incorporates robust progress monitoring. A visual feedback mechanism, typically a dynamic progress bar, displays the operation’s advancement in real time. This transparency is critical for managing expectations, especially when dealing with large firmware images or slower SD card interfaces. It confirms that the tool is actively engaged and prevents users from prematurely terminating processes that could lead to corrupted media.
Integrated Demo and Verification Functionality
The inclusion of optional demo functionality serves as an embedded quality check. This feature allows users to execute a simulation or a limited run-through of the intended operation without necessarily committing to a full, high-stakes deployment. For testing environments, this can validate that the generated boot media interacts correctly with the device’s boot sequence, confirming partition alignment and initial hardware handshake before committing resources to a full production flash.
Comprehensive Restoration and Recovery Capability
Perhaps one of the most safety-critical features is the restore capability. In complex embedded development, firmware flashing can occasionally fail due to power interruption, driver issues, or incompatible source images. The tool is designed to facilitate recovery by allowing users to revert the SD card to a previously known good state or to re-initialize the card structure following a failed operation. This built-in recovery mechanism acts as a safeguard, preventing an improperly flashed card from becoming permanently unusable and minimizing downtime associated with recovery procedures.
Accessibility and Version Control
The utility is designed to be accessible across common Windows environments, supporting both 32-bit and 64-bit architectures, ensuring broad compatibility with existing technician workstations. The provision of multiple versions (1.4, 1.53, and 1.7) indicates an active development and maintenance cycle, reflecting updates to support newer Rockchip chipsets, address security vulnerabilities, or incorporate enhanced hardware compatibility layers. Users are generally advised to utilize the latest available version (1.7, in this instance) unless specific legacy hardware mandates an older release.
| Version | Download Link |
|---|---|
| 1.4 | [Link to RockChip Create Upgrade Disk v1.4] |
| 1.53 | [Link to RockChip Create Upgrade Disk v1.53] |
| 1.7 | [Link to RockChip Create Upgrade Disk v1.7] |
The availability of these direct download links streamlines the procurement process for necessary development assets. Selecting the correct version hinges on matching the tool’s supported chipset list—often detailed in accompanying release notes not included here—with the specific Rockchip SoC powering the target hardware. The tool’s enduring relevance underscores the fact that, even as devices evolve, the fundamental requirement for reliable, low-level media preparation remains a constant in the world of Rockchip-based system development and maintenance. Its structured feature set ensures that the creation of robust, bootable SD cards is an efficient and auditable process.